yFiles Layout Algorithms
for Cytoscape
The yFiles Layout Algorithms for Cytoscape app brings the layout algorithms of the renowned yFiles diagramming libraries to Cytoscape!
Now one click is all you need to arrange your Cytoscape networks in a clear and concise
way with the yFiles layout algorithms and edge routing algorithms at your disposal.
The yFiles diagramming libraries are world-class software components for arranging and visualizing graph structures. They come with a suite of highly sophisticated and highly customizable layout algorithms.
Use of the yFiles Layout Algorithms for Cytoscape app is subject to this Software License Agreement.
Get the app from the Cytoscape app store .
DownloadThe Layout Algorithms
The following major yFiles layout algorithms and edge routing algorithms are available with the app:
Circular Layout

The Circular layout algorithm portraits interconnected ring and star topologies. This algorithm produces layouts that emphasize group and tree structures within a network. It creates node partitions by analyzing the connectivity structure of the network and arranges the partitions as separate circles or disks.
Hierarchic Layout
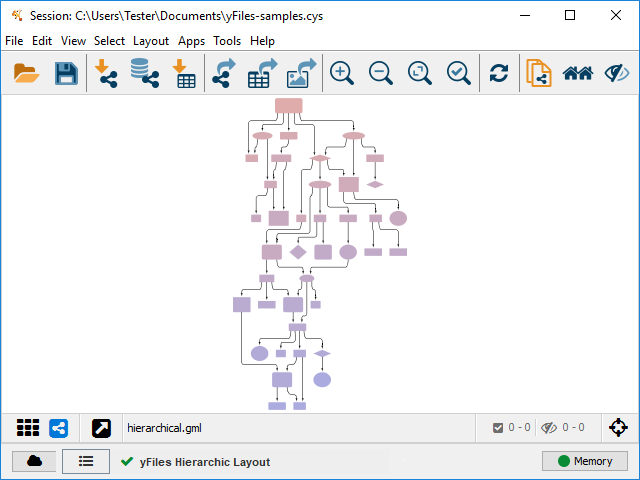
The Hierarchic layout algorithm portraits the precedence relation of directed graphs. Use this algorithm to highlight the main direction or flow within a directed graph. Cyclic dependencies of nodes will be automatically detected and removed. Nodes will be placed in hierarchically arranged layers. Additionally, the ordering of nodes within each layer is chosen in such a way that the number of edge crossings is small.
Hierarchic Layout Selected Nodes
Hierarchic layout (for) selected nodes is a variant of the classic hierarchic layout described above. Compared to the classic hierarchic layout which computes an all-new, fresh graph layout each time it is invoked, this variant will rearrange the sub-graph induced by selected nodes while the remainder of the graph is not, or only slightly, changed. This technique makes it possible to maintain the user's so-called "mental map" over a course of subsequent graph layout calculations.
Organic Layout
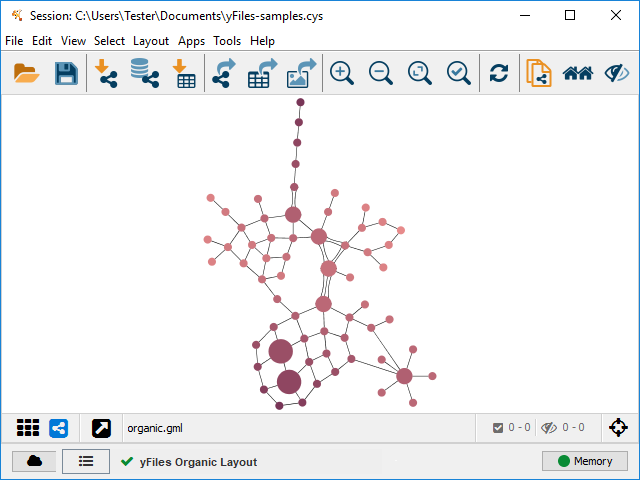
The Organic layout algorithm is a multi-purpose layout style for undirected graphs. The algorithm is based on the force-directed layout paradigm. When arranging a graph, nodes are considered to be physical objects with mutually repulsive forces, like protons or electrons. The connections between nodes also follow the physical analogy and are considered to be metal springs attached to pairs of nodes. These springs produce repulsive or attractive forces between their endpoints if they are too short or too long. The algorithm simulates these physical forces and rearranges the positions of the nodes in such a way that the sum of the forces emitted by the nodes and the edges reaches a (local) minimum.
Orthogonal Layout
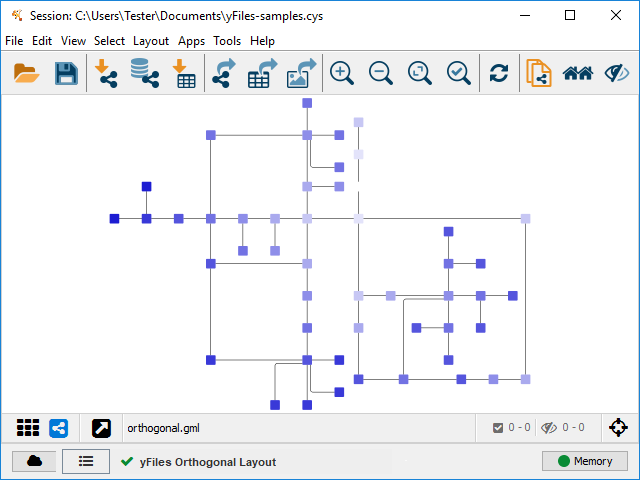
The Orthogonal layout algorithm is a multi-purpose layout style for undirected graphs. The algorithm is well suited for medium sized sparse graphs. It produces compact drawings with no node overlaps, few crossings, and few bends. All edges will be routed in an orthogonal style, i.e. only vertical and horizontal line segments will be used.
Radial Layout
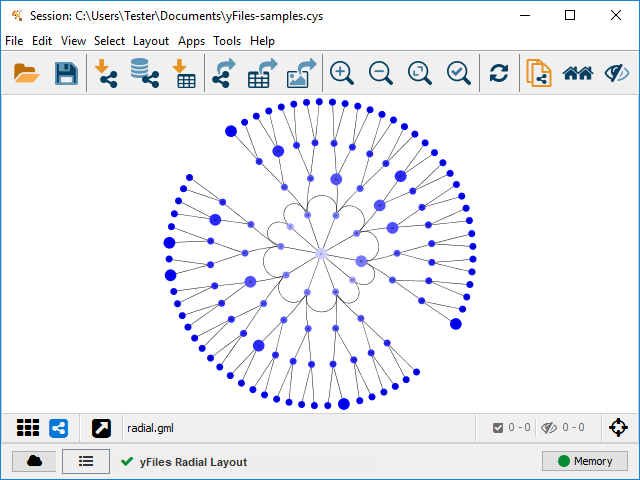
The Radial layout algorithm places nodes on virtual concentric circles around a common center. This algorithm emphasizes tree structures within a diagram.
Tree Layout
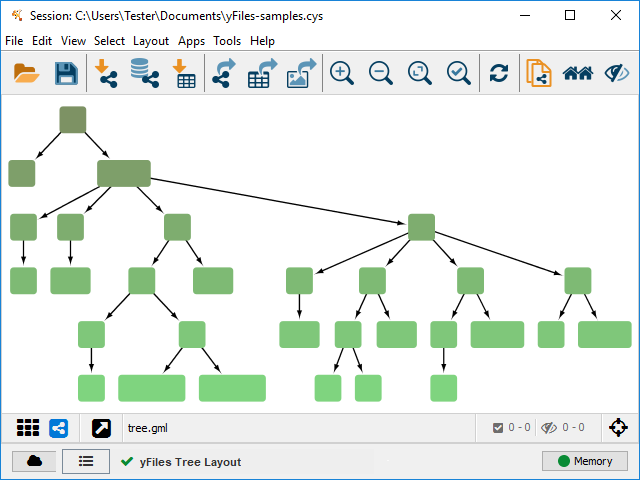
The Tree layout algorithm is especially suitable if the input graph is a tree or a collection of trees. A tree is a graph that contains no undirected cyclic edge path. If the input graph is not a tree, it is transformed into one by temporarily removing some edges.
Orthogonal Edge Router

The orthogonal edge routing algorithm can route the edges of a diagram using vertical and horizontal edge segments while keeping the positions of the nodes in the diagram fixed. The routed edges will usually not cross through any nodes.
Organic Edge Router
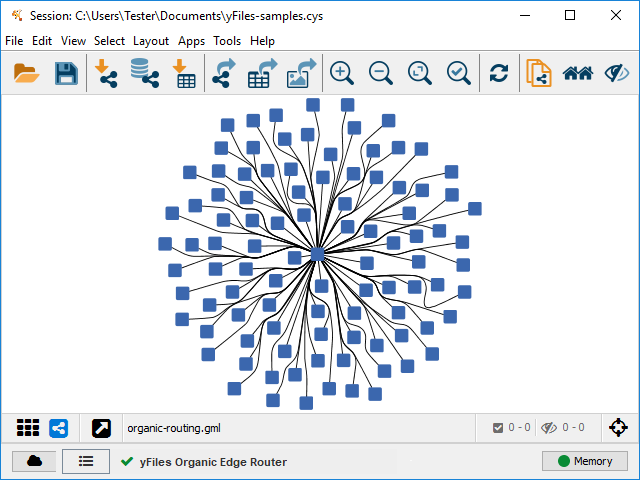
The organic edge routing algorithm routes edges organically to ensure that edges do not overlap nodes and keep a certain minimal distance between them. It is especially well-suited for non-orthogonal, organic, or cyclic layout styles. The algorithm is based on a force-directed layout paradigm. Nodes act as repulsive forces on edges in order to guarantee a certain minimal distance between nodes and edges. Edges themselves tend to contract themselves. Using simulated annealing this leads to edge layouts, which are calculated for each edge separately.
About yWorks
yWorks is the maker of the yFiles family of diagramming software components and a decent number of fine tools.
The yFiles diagramming software components enable you to add high-quality diagramming functionality
to your own software applications: turn your data into clear diagrams with the help of unequaled
automatic diagram layout, use rich visualizations for your diagram elements, and give your
users an intuitive interface for smooth interaction.
yFiles is available for a wide range of platforms and technologies: from web-platform
to java-platform to the Microsoft .NET-platform.
you might want to explore
Why, how, what? —Just ask the diagramming experts!
Our team is happy to advise you – no strings attached. Let's talk about your project and find the perfect solution for your needs!
E-mail: hello@yworks.com
Your message has been sent.
Your request could not be sent. Please reload the page and try again.
If the problem persists, please report the error to webmaster@yworks.com.
Learn more in our privacy policy.